5G and the Internet of Things
The IoT, or Internet of Things, has developed to encompass a multitude of use cases for the enterprise, industrial and consumer spaces. In the enterprise and industrial spaces; strategic decisions now incorporate the inclusion of IoT services and connectivity, which has been driven in no small part by the emergence of IoT specialists.
The consumer space has also been significantly disrupted during the past five years. Declining costs of wireless networks and innovation in technology, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, mean that an increasing number of previously ‘dumb’ devices are being connected to the Internet or a private network.
5G networks, first launched in 2019, offer new benefits for existing technologies including:
The consumer space has also been significantly disrupted during the past five years. Declining costs of wireless networks and innovation in technology, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, mean that an increasing number of previously ‘dumb’ devices are being connected to the Internet or a private network.
5G networks, first launched in 2019, offer new benefits for existing technologies including:
- High bandwidth and throughput
- Ultra-low latency
- Energy consumption and battery life
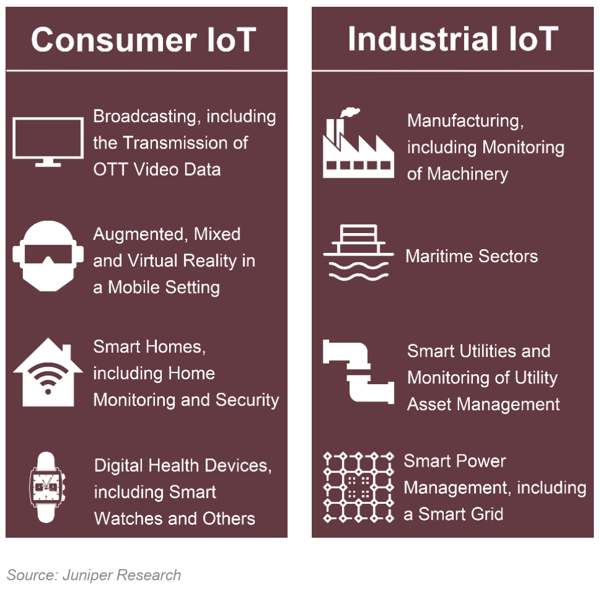
As shown in Figure 1, there are new IoT use cases that will be driven by the emergence of 5G networks
in many verticals.
Indeed, the ability to provide high bandwidth and low latency in a mobile setting will prove incredibly attractive to a number of other service providers.
Figure 1: Examples of Consumer & Industrial IoT Use Cases Enabled by 5G Connectivity
1.1 - The Impact of 5G Networks on IoT
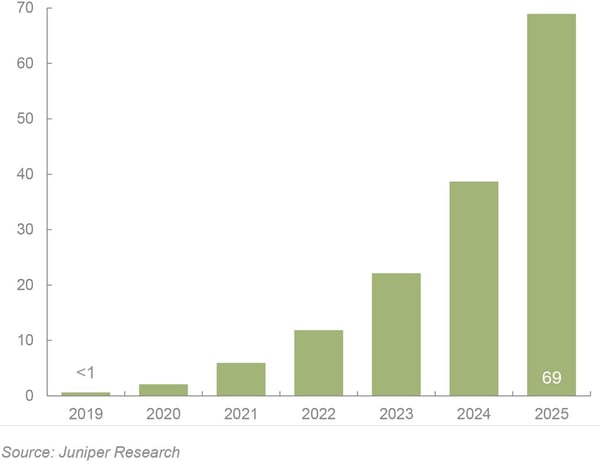
The impact of 5G networks cannot be understated when considering the new use cases it can enable. Juniper Research believes that the global number of 5G connections will grow from less 1 million connections in 2019 to nearly 70 million in 2025.
Figure 2: Global 5G Commercial IoT & Automotive Active Connections (m) 2019-2025
 However in the context of the wider IoT, the number of 5G connections will only be a small proportion of all IoT connections. There are many technologies that will underpin IoT connectivity, including:
However in the context of the wider IoT, the number of 5G connections will only be a small proportion of all IoT connections. There are many technologies that will underpin IoT connectivity, including:- LTE networks
- Cellular LPWA (Low Power Wide Area)
- Other cellular networks, such as 2G or 3G
- Bluetooth
- Unlicensed networks
- Fibre connectivity
From the perspective of IoT network users, cost of connectivity plays a huge role in how new connections are added to the network. Juniper Research believes that 5G connections will only be used when either high bandwidth or ultra-low latency is a necessity. However; complementary technologies, such as as low power alternatives, fibre networks or unlicensed wireless technologies, will all contribute to a comprehensive solution.
Additionally, cellular connections require a monthly subscription unlike alternative technologies such as Bluetooth or fibre connectivity. As a result, these technologies will become increasingly attractive to potential new users as they seek strategies to secure a return on their investment in IoT technologies.
5G networks have been developed to be scalable and to efficiently support the large number of connections and the variety of use cases for which they will be used. Juniper Research believes that IoT service providers will need to re-evaluate their service offerings to ensure they can serve these new 5G connections. These services include network slicing and eSIMs (embedded SIMs). In the future, SDNs (Software Defined Networks), cloud technologies and specialized network applications will all work together to provide an IoT service that fits a multitude of industries.
Therefore, we can say that the addressable user base for 5G IoT connections can be considered largely a different subset to those who existed before the advent of 5G.
The capabilities of 5G networks are unprecedented in a mobile setting; the new 5G connections can be considered entirely new IoT connections. This can provide an entirely new revenue stream for operators as they seek this crucial return on investment from 5G networks.
Juniper Research believes that other connectivity will also play a key role alongside 5G networks in growing the number of connected devices. The connectivity used will be wholly dependent on the nature of the device itself. The wider IoT ecosystem will leverage technologies such as LPWA, 2G, 3G and unlicensed networks to provide connectivity.
Telna is introducing the concept of 5G into its core network, enabling services to be brought closer to both the edge of the network and the user. This enables users to access network applications faster over Telna’s network.
1.2 - Quantifying 5G Data Traffic in the IoT
As the high bandwidth of 5G is a key differentiating factor over other IoT connectivity technologies, the issue of carrying large amounts of data will be a challenge for network operators.
Markets including AR (Augmented Reality) and VR (Virtual Reality) are also dependent on high-bandwidth connections, so these are likely to use 5G rather than alternative technologies. However, industries such as Smart Cities and Smart Homes have varying use cases, meaning that 5G will not always be desirable for stakeholders for each use case.
Markets including AR (Augmented Reality) and VR (Virtual Reality) are also dependent on high-bandwidth connections, so these are likely to use 5G rather than alternative technologies. However, industries such as Smart Cities and Smart Homes have varying use cases, meaning that 5G will not always be desirable for stakeholders for each use case.
Mobile Edge Computing to Lessen Dependence of 5G Networks
Edge computing places network functions at the edge of the network closer to the end nodes (5G connections), which reduces strain closer to the network core. When the large quantities of data generated by 5G networks is considered, mobile edge computing will become necessary to handle this data.
Figure 3: Mobile Edge Computing Architecture
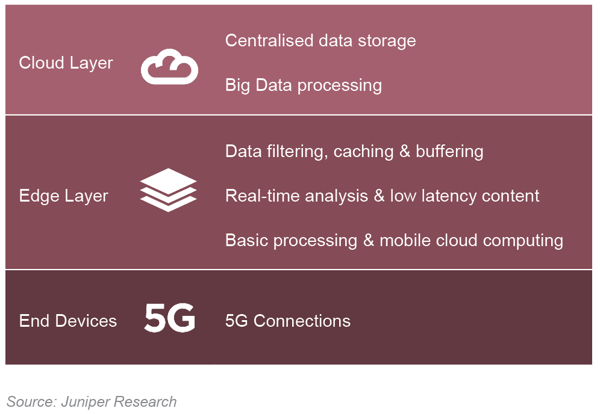
The investment needed to set up a robust edge computing network is significant, especially in instances where operators cover large geographical regions. Nevertheless, the benefits of early mover advantages in mobile edge computing cannot be understated.
In addition to placing computational, or processing power, at the end of the network, edge computing would allow high demand content to be placed at the edge of networks. This would allow content to be downloaded and rendered at a faster rate to further improve the user experience.
Follow @TelnaGlobal on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn and Instagram for the latest news.
Telna
Telna provides Mobile Network Operators (MNOs), Communication Service Providers (CSPs), and Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) with a fully managed global cellular connectivity platform. Telna has the largest 2G – 5G, LTE-M to over 800 radio network operators – 300 in direct partnerships – in 200 countries. Its global multi-network connectivity platform enables simplified integration to any platform and enables local break-out with localization that utilizes cloud infrastructure. With one integration to Telna’s platform, we have enabled millions of devices with multi-network connectivity, enabling innovative solutions in the cloud.
COMMENTS
